Publication – Utilising moving vehicles to distribute video processing applications
Tags:
Outline the paper
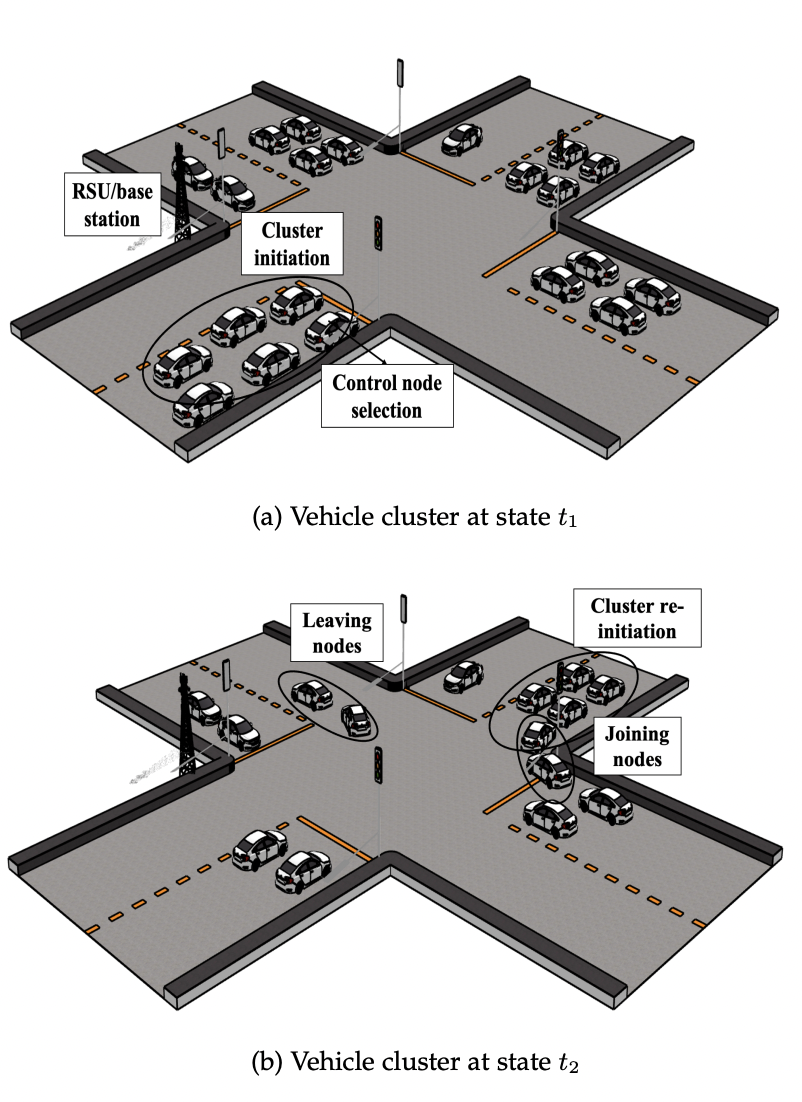
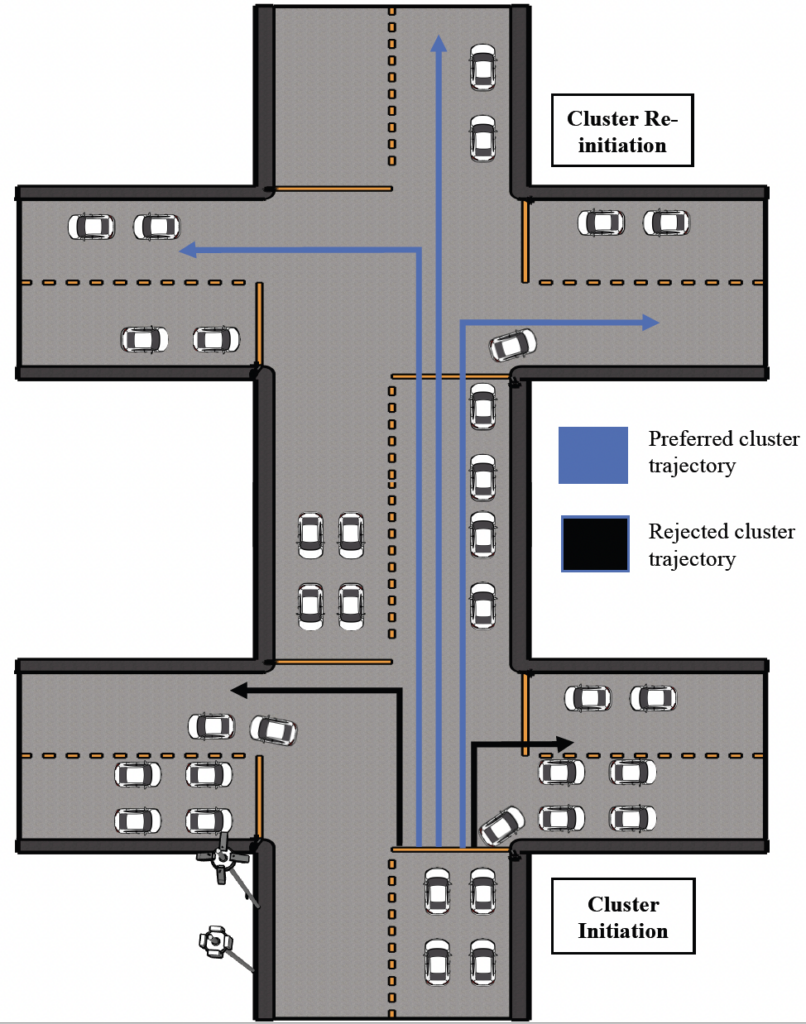
Currently, most of the data for monitoring traffic and road conditions is collected through static infrastructures like video cameras and loop detectors. To reduce the cost of installing additional infrastructure, and to utilise the embedded resources in smart vehicles, we introduce a Vehicular Fog Computing (VFC)-based service placement plan. We study the mobility patterns of vehicles at urban intersections in cities like Dublin. Using the historic mobility patterns of vehicles, we select those vehicles that are more likely to stay together. We then deploy novel data collection and processing services on these vehicle clusters.
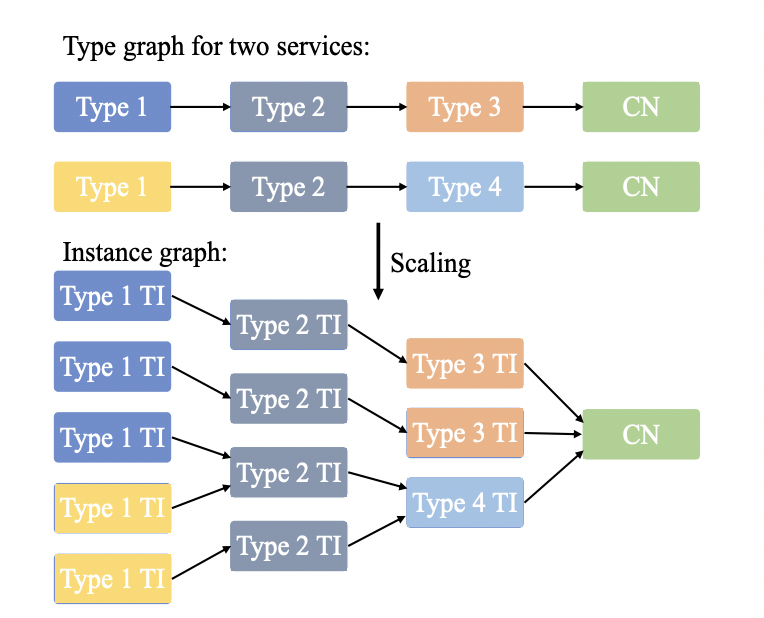
In this publication, VFC is envisioned as an extension of cloud and mobile edge computing to utilise the rich sensing and processing resources available in vehicles. We focus on slow-moving cars that spend a considerable time in urban traffic congestion as a potential pool of onboard sensors, video cameras, and processing capacity. To leverage the dynamic resources in a closely-moving group of vehicles, we utilise a stochastic mobility model to select nodes with similar mobility patterns. We then design two novel and distributed applications for data collection and object detection to be placed on the selected vehicular fog nodes.
Who will it help?
Since commuters spend a significant amount of time in urban traffic, they can benefit from a vehicular-fog marketplace, where vehicle owners will be incentivised in return for leasing their sensing and processing resources. Such services can benefit transport authorities and enable them to collect and utilise data to manage cities better. The commuters leasing their resources can be provided with free parking or their toll charges can be waived as an incentive for crowdsensing and processing data.
What is the future of this research?
In future work, we plan to extend our theoretical treatment of mobile service placement on vehicles in urban traffic by collecting data from a smart city testbed and analysing how well our algorithm performs in practice. We also intend to consider service migration, and not just the initial service placement problem. We intend to add the role of multiple road side units to manage the life cycle of both the control nodes and the vehicle cluster.
These applications can report on traffic conditions at peak and off-peak hours; help study the usage patterns of roadside fuel stations, cafes, and shopping centres; and can be used to detect vulnerable pedestrians and cyclists, alerting nearby drivers to increase the safety of commuters.
This publication has emanated from research conducted with the financial support of the Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) funded CONNECT project.
Publication Title: Graph-based Heuristic Solution for Placing Distributed Video Processing Applications on Moving Vehicle Clusters
Authors: Kanika Sharma, Bernard Butler, Brendan Jennings
Publication Date: 10 May 2022
Name of Conference: IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management
Link to publication: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9771209